Statistical Legislation
Well-developed national legislation regulating the production of official statistics is necessary to ensure the implementation of the principles described in Chapter 3.2 — UN Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics. The overall target is to ensure the production of official statistics with a high level of quality, meeting users’ needs and being trusted by users and other stakeholders.
A successful national statistical system should have the flexibility to respond to changing conditions and circumstances without needing to change its primary legislation frequently. A flexible legal environment minimizes legislation changes and the associated risk of political interference with the legislation when it is opened for revision.
The legislation in the field of official statistics may have cross-linkages with the other legislation not directly related to statistics. Other legislation might conflict with the statistical legislation, with the risk of hindering the coordination and functioning of the NSS. Thus, when revising or updating the statistical legislation, these cross-linkages must be carefully taken care of.
“The subject of statistical legislation can be reduced to two major issues: the compulsory aspect, that is, the power the government asserts through the statistical agency to collect data; and the guarantees it provides for safeguarding the confidentiality of the information collected from individual respondents…”
(unstat.un.org)
Statistical Legislation in CARICOM
Reliable, timely and comparable statistics are essential to evidence-based decision-making, effective governance, and the sustainable development of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). To strengthen the regional statistical system and ensure that Member States are equipped to meet evolving data needs, CARICOM has advanced comprehensive efforts to modernise and harmonise statistics legislation across the Community.
Modernising the Statistical Framework
CARICOM has developed a Model Statistics Bill designed to support Member States in updating outdated legislation and establishing a modern legal framework for the production, management, and dissemination of official statistics. The Model Bill promotes consistency across national statistical systems while respecting each country’s legal and institutional context.
designed to support Member States in updating outdated legislation and establishing a modern legal framework for the production, management, and dissemination of official statistics. The Model Bill promotes consistency across national statistical systems while respecting each country’s legal and institutional context.
Promoting Regional Harmonisation
Harmonised legislation supports more consistent statistical methodologies, classifications and standards across Member States. This alignment is critical for producing comparable regional data on key areas such as population, labour markets, trade, health, education, crime, the environment and sustainable development indicators.
A harmonised legal framework also strengthens the CARICOM Regional Strategy for the Development of Statistics (RSDS), which sets out the long-term vision for a coordinated, modern and resilient regional statistical system.
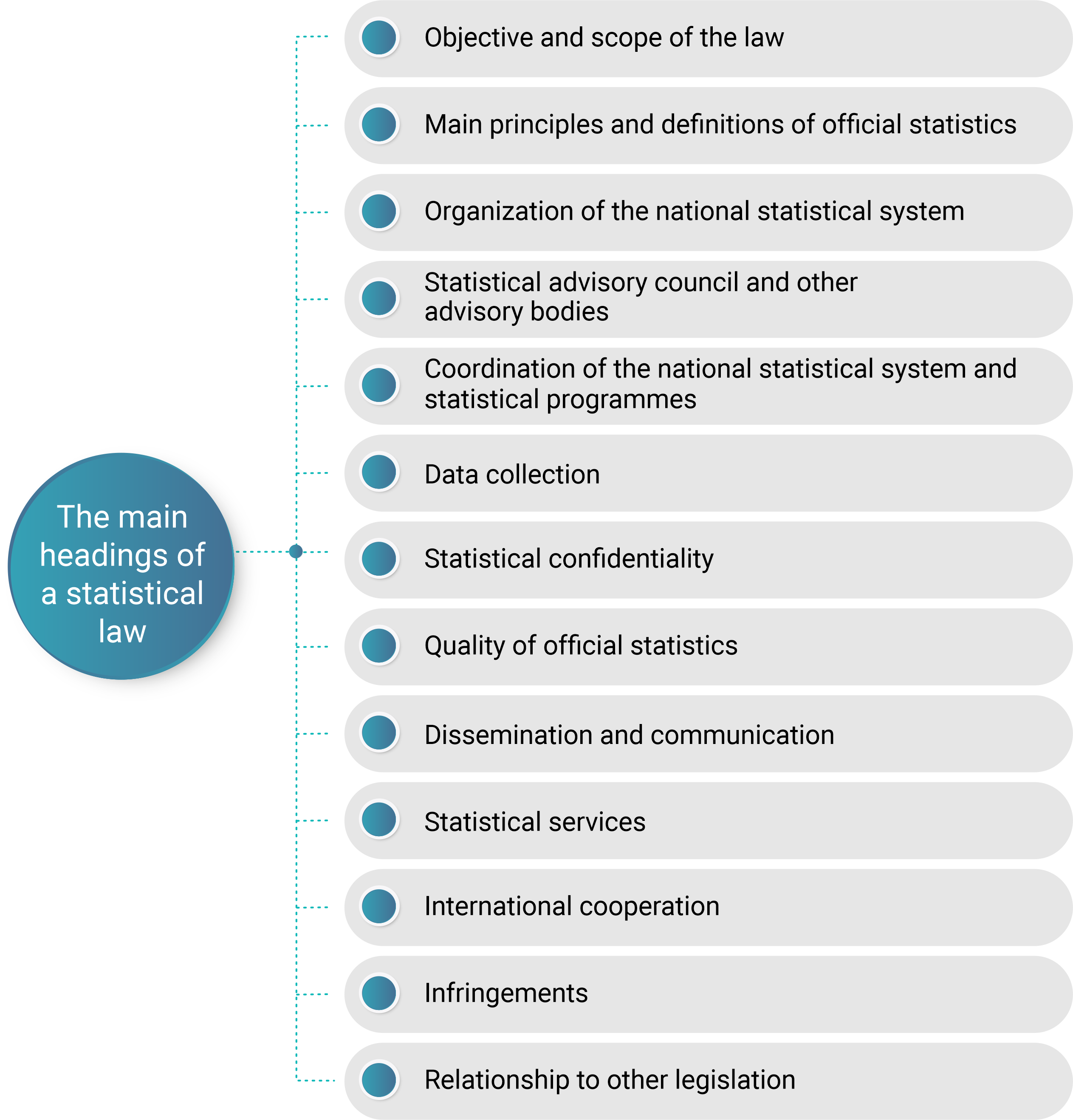
Statistical law or act
It is a specific document of statistical legislation of a country passed by the legislative body (e.g., parliament, general assembly, congress, house of representatives, house of the senate, etc.) or any legally-recognized institution with similar function or power.




 designed to support Member States in updating outdated legislation and establishing a modern legal framework for the production, management, and dissemination of official statistics. The Model Bill promotes consistency across national statistical systems while respecting each country’s legal and institutional context.
designed to support Member States in updating outdated legislation and establishing a modern legal framework for the production, management, and dissemination of official statistics. The Model Bill promotes consistency across national statistical systems while respecting each country’s legal and institutional context.